Types of Power Generation Sources - Their Advantages and Disadvantages
1. Non-Renewable Power Generation
Non-Renewable forms of
energy production are dependent on limited resources, which will ultimately
deplete. Additionally, they have a significant share of the blame for
greenhouse gas emissions. The type of Non-Renewable
Power Generations are
- Thermal Power
Generation
Steam is produced during the
thermal power production process by burning fossil fuels like coal, oil, or
natural gas. A turbine is spun by the steam, producing energy. The most
prevalent and most polluting kind of power plant in the world is the thermal
power station.
Advantages:
Fuel sources are easily
accessible and the technology is dependable and advanced. comparatively little
initial outlay for building a factory.
Disadvantages:
substantial amounts of greenhouse
gases, a factor in climate change. When fossil fuels are used, air pollution
can be harmful to human health. depletion of fossil fuels, such as natural gas
and coal.
- Nuclear Power
Generation
Nuclear fission, or the splitting
of atomic nuclei, is the process used in nuclear power generation to produce
heat. After that, the heat is used to produce steam, which turns a turbine to
provide energy. While in operation, nuclear power facilities do not emit
greenhouse gases, but they do create radioactive waste and cause safety issues.
Advantages:
High energy density, producing a
lot of electricity from a tiny quantity of fuel. No greenhouse gas emissions
when the system is in use.
Disadvantages:
Exorbitant up-front expenses
associated with building and decommissioning plants. Risk of catastrophic
nuclear mishaps that could occur. The disposal of radioactive waste presents
long-term environmental challenges.
2. Renewable Power Generation
Renewable
energy is produced from resources including sunshine, wind, rain, tides, waves,
and geothermal heat that are naturally regenerated on a human timescale. The
importance of renewable energy sources is rising as we try to fight climate
change and lessen our dependency on fossil fuels.
- Solar Power
Generation
Photovoltaic (PV) cells are used in solar power generation to directly convert sunlight into electricity. Solar photovoltaic systems can be incorporated into building materials or put on rooftops or in the ground. Although solar energy is an intermittent energy source that only generates electricity when the sun is shining, it is still a clean and sustainable energy source.
Rooftop solar panels can be installed in any place like houses, industries, farms, etc. you just need to contact a best solar panel installers near you.
Advantages:
Advantages include a clean, renewable energy source with no effect on the environment. has a long lifespan and needs little upkeep. increasing solar panel affordability.
Disadvantages:
sporadic energy source that depends on sunshine availability. comparatively lower energy density than fossil fuels. need a substantial amount of land in order to operate huge solar farms.
- Wind Power
Generation
Wind turbines are used in wind power generating to transform wind energy from kinetic to electrical energy. The wind propels the blades of wind turbines, which turn a shaft that powers a generator. Although wind power is an environmentally friendly and sustainable energy source, it is only able to generate electricity when there is wind.
Advantages:
Low environmental impact, clean, renewable energy source. able to be installed anywhere there is enough wind power. The efficiency of wind power is increasing due to technological developments.
Disadvantages:
Dependent on wind speed, intermittent energy source. can impede bird migration patterns and be visually intrusive. Wind turbine noise can be an issue for the local population.
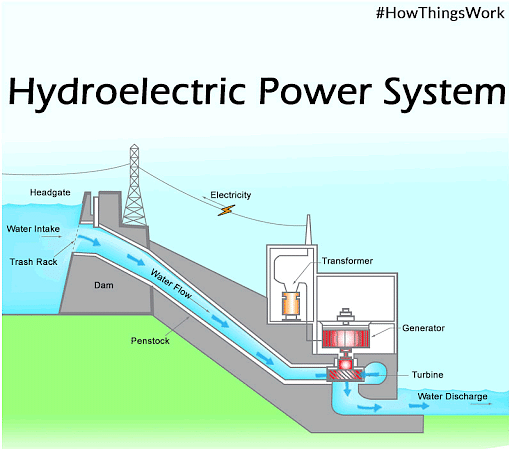
- Hydropower
Generation
The energy of flowing water is harnessed in hydropower generation to produce electricity. Hydropower dams spin turbines to produce energy using the gravitational force of falling water. Although hydropower is an established and trustworthy renewable energy source, river flows and ecosystems may suffer as a result of its use.
Advantages:
High energy density renewable energy source that is mature and dependable. offers further advantages like flood control and water storage.
Disadvantages:
May destroy river flows and habitats, which may have an impact on fish populations. Dam construction can affect land usage and force communities to relocate. restricted ability to build additional hydropower plants because of geographic limitations.
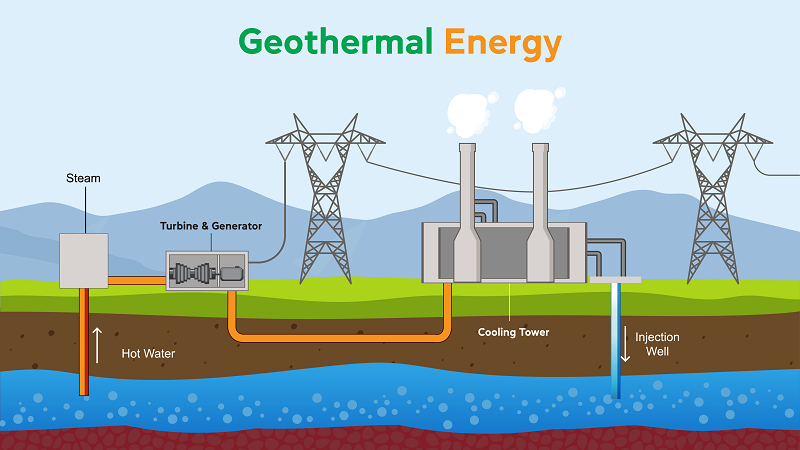
- Geothermal Power
Generation
Geothermal power generating produces electricity by harnessing heat from the Earth's interior. Geothermal power facilities use steam or hot water from subterranean reservoirs to run turbines that produce energy. Although it is only available in places with geothermal resources, geothermal power is a dependable and clean renewable energy source.
Advantages:
Low emissions, clean, dependable renewable energy source. It is long-lasting and unaffected by weather.
Disadvantages:
Only available in areas with geothermal resources. Exploration and plant construction might have significant upfront expenses. Potential for negative effects on the environment, such as water contamination in some places or seismic activity.
- Bioenergy
Generation
Utilizing biomass—such as wood, crops, or manure—bioenergy generation generates electricity. Alternatively, biomass can be processed into biogas or biodiesel, which can be used to produce power, or it can be burned straight to produce steam. Although bioenergy is a renewable energy source, it can exacerbate air pollution and deforestation.
Advantages:
Organic waste materials can be utilized as a renewable energy source. can support rural development and energy independence.
Disadvantages:
If biomass burning is not managed properly, it can produce air pollutants and contribute to deforestation. Food crops and large-scale production may compete for land utilization.
- Tidal and Wave
Power Generation
Tidal and wave power generating harness the energy of tides and waves to create electricity. The ebb and flow of the tides power turbines in tidal power plants. Wave power plants employ machinery to harvest wave energy. Although they are still in their infancy, wave and tidal power are potential renewable energy sources.
Advantages:
High energy density, predictable, renewable energy sources. Minimal land-use effect compared to other renewable sources.
Disadvantages:
Expensive up-front expenses and early development stage. Efficiently capturing and converting wave and tidal energy still presents technological obstacles. More research is required to determine potential environmental effects on marine species and ecosystems.
Final Words:
The availability of resources, the effect on the
environment, and the viability of the project economically all influence the
choice of power producing method. Future energy production will probably come
from a variety of renewable sources, with an emphasis on sustainability and
efficiency, as technology develops further.